Video Link: https://vimeo.com/557221988
Video Download: Peptide Yy Function And Therapeutic Potential
Video Stream: Peptide Yy Function And Therapeutic Potential
Pancreatic Peptide YY is one of many hormones involved in the digestive activity. It is produced by L-cells along with a handful of other hormones. These cells are primarily located in the ileum and colon.
Also referred to simply as Peptide YY, this important hormone is released in response to 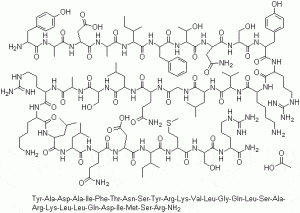 eating. Peptide YY is responsible for sending signals from the digestive tract to the brain in order to signal the feeling of fullness.
eating. Peptide YY is responsible for sending signals from the digestive tract to the brain in order to signal the feeling of fullness.
When Peptide YY acts on the brain, it induces the sensation of fullness and suppresses appetite. Peptide YY also operates within the digestive system itself, slowing down the rate by which food passes through the Gastrointestinal Tract. Peptide YY is released in tandem with Glucagon-like peptide 1, which is very important to glucose management.
Modulation of Peptide YY
Peptide YY is intricately involved in the digestive activity. The digestive system releases the hormone as food enters and passes through the GI Tract. It responds strongest to the presence of protein and fat, and it is less responsive to carbohydrates.
Peptide YY activity is positively correlated with caloric consumption. Calorie-dense foods release more Peptide YY into the bloodstream than foods with fewer calories.
Peptide YY Levels also increase in the presence of digestive fluid and cholecystokinin. Cholecystokinin is released by duodenum cells and activates the pancreas to produce enzymes and the liver to secrete bile.
Circulating Peptide YY is fairly predictable. Levels are at their highest around two hours after eating and slowly drop over time. Peptide YY levels are at their lowest after long durations without food, especially upon waking up from sleep.
The Effects of Peptide YY Abnormalities
Under normal circumstances, Peptide YY performs dutifully. Some people produce too much or too little Peptide YY, however.
Abnormally low Peptide YY Levels are more common than having chronically high levels of the hormone. Elevated Peptide YY is associated with IBS, Celiac Disease, and anorexia, along with some forms of cancer, and leads to reduced appetite.
When Peptide YY Levels are chronically low, it suppresses feelings of satiety and frequently leads to weight gain. Most commonly, clinically low Peptide YY levels are associated with Pre-Diabetes, Type-2 Diabetes, and Obesity.
Current research suggests that Suppressed Peptide YY Levels are a secondary effect of  obesity, which can be corrected by weight loss.
obesity, which can be corrected by weight loss.
Could Peptide YY Be Used for Weight Loss?
Peptide YY shows some promise as a potential treatment for obesity. The goal of prescription Peptide YY would be to mitigate feelings of hunger to make it easier to stave off hunger and cravings.
Some ongoing studies use a combination of gastrointestinal hormones known as GOP as a potential means to help men and women lose weight. GOP is an acronym for GLP-1, oxyntomodulin, and Peptide YY. This treatment shows promise for both encouraging significant weight loss and controlling blood sugar.
Contact Us For A Fast And Professional Response

- Peptide Primer: Getting a Boost From Peptides [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 6th, 2021]
- Tesamorelin Testimonial by Vincent "Coach Vinny" Jones [Last Updated On: January 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 21st, 2022]
- BPC-157: A Potent Peptide Therapy for Men’s Hormone Health [Last Updated On: January 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 26th, 2022]
- Unveiling the Anti-Aging Secrets: The Role of Peptides in Modern Medicine [Last Updated On: February 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 16th, 2025]
- Peptides and Epigenetics: Enhancing American Men's Health and Disease Prevention [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 19th, 2025]
- Peptide Innovations: Transforming Allergy Management in American Males [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- The Unveiling Frontier: Peptides in the Panorama of Future Medicine [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Exploring the Role of Peptides in Diabetes Management: Advancements and Future Directions [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Peptide Therapeutics: Transforming Neurological Disorder Treatments in American Males [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Peptide-Based Immunotherapy: Revolutionizing Treatment for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Exploring Peptide Therapy in Men's Health: Applications and Future Directions [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Peptide-Based Antimicrobials: Targeted Solutions for American Men's Health Challenges [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Peptides: The Key to Men's Youthful Skin - Dermatological Insights and Benefits [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Revolutionizing Men's Health: Harnessing Biomimetic Peptides for Tissue Regeneration and Healing [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Advancements in Therapeutic Proteins and Peptides: Navigating Challenges for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Unlocking the Potential of Peptides in Precision Medicine for American Males [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Unlocking the Power of Peptides: Revolutionizing Wound Healing and Tissue Repair in American Males [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Peptides and Metabolic Health: A New Frontier for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Peptide Therapies: A New Hope for Managing Obesity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Peptides in Veterinary Medicine: Innovations for American Male Veterinarians [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Peptide and Stem Cell Synergy: Revolutionizing Regenerative Medicine for American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Peptide Therapeutics: Revolutionizing Chronic Disease Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Peptides: A New Frontier in Managing Respiratory Health for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Peptides: Enhancing Immune Response and Therapy for American Males Against Infections [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Peptide Vaccines: Advancements, Challenges, and Future for American Males' Immunization [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Peptides and Gene Therapy: Revolutionizing Men's Health in America [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Peptides Revolutionizing Eye Care for American Males: Current Research and Future Hope [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Peptides in Medicine: Enhancing Diagnostics and Drug Delivery for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Peptides Offer Hope for Managing Neuropathic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Peptides Revolutionizing Dental Care for American Males: Healing and Regeneration [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Peptide Therapy: Enhancing Men's Health from Muscle to Cancer Treatment [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Peptide-Enriched Skincare: A Scientific Approach for American Men's Grooming Needs [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Peptides: Enhancing Gut Health and Microbiome Balance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Peptide Therapeutics: Targeted Treatments for Rare Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Peptides: A New Frontier in Mental Health Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Topic Peptides: A Promising New Treatment for Rheumatic Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Peptide-Based Biomarkers: Revolutionizing Disease Detection in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Peptides Revolutionizing Epilepsy Treatment for American Males: New Hope and Insights [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Peptide-Based Biosensors: Revolutionizing Health Monitoring for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Peptide Nanotechnology: Revolutionizing Medicine for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Peptide Drugs in Pediatrics: Targeted Treatments for Growth and Metabolic Disorders [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Peptide Radiopharmaceuticals: Revolutionizing Men's Health with Targeted Imaging and Therapy [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Bioactive Peptides: A New Frontier in Men's Health and Wellness [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Peptides: A New Frontier in Cardiovascular Disease Prevention for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Peptide-Based Anti-venoms: A Promising Leap in Treating Snakebites for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Peptides: A New Frontier in Liver Health Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Peptide Therapy with Topic Peptides for Hematological Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Peptides and Male Fertility: Enhancing Reproductive Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Peptides: Unlocking Potential in Men's Health and Anti-Aging Treatments [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Peptide Therapies Enhance Bone Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Next-Generation Peptide Therapies Enhancing Transplant Outcomes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Peptides in Endocrinology: Therapeutic Advances for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Peptides: A Promising Solution to Antibiotic Resistance for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Peptide Therapies: A New Frontier in Treating GI Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Peptides: A Promising New Approach to Managing Inflammation in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Peptides in Sports Medicine: Enhancing Performance and Recovery for American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Peptide-Polymer Composites: Revolutionizing Medicine for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Peptides: A Promising New Frontier in Treating Male Hair Loss [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Peptide-Based HIV Vaccines: Progress and Hope for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Peptides in Trauma Medicine: Enhancing Healing and Recovery for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Peptide Research Advances Offer Hope for American Men with Neurodegenerative Diseases [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Stem Cells and Peptides: Enhancing Men's Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Peptide Bioinformatics: Revolutionizing Precision Medicine for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Peptides Revolutionizing Stroke Treatment and Recovery in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Peptides as Cell-Penetrating Agents: Revolutionizing Drug Delivery and Targeted Therapies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Peptides Revolutionize Toxicology: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Vaccines for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Peptide-Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy: A Targeted Approach for American Males' Cancer Treatment [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Peptide Vaccines: Revolutionizing Veterinary Medicine with Targeted Immunization [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Peptides' Role and Therapeutic Potential in Managing Acute Kidney Injury in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Peptide Drug Conjugates: Revolutionizing Men's Health with Targeted Therapy [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Peptides in Substance Abuse Treatment: Mechanisms, Efficacy, and Future Prospects for American Males [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Peptides in Burn Care: Enhancing Healing and Scar Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Peptide Therapies: A New Hope for Autoimmune Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Peptide Therapies: Advancing Prostate Cancer Treatment with Precision and Promise [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Peptide Therapy: A Promising Approach to Osteoporosis in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Peptides in Geriatric Medicine: Enhancing Health in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Peptides: A Promising New Treatment for Ocular Infections in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Peptides in Veterinary Dermatology: Benefits, Challenges, and Future for American Pet Owners [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Peptide Therapy: A Promising Future for Treating Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Peptides Revolutionize Post-Operative Recovery for American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
















