Introduction
Primary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the failure of the testes to produce adequate levels of testosterone, has been a subject of extensive research due to its significant impact on male health. Recent studies have begun to explore the intricate relationship between primary hypogonadism, estrogen levels, and aromatase activity. This article delves into a comprehensive analysis of over 3,000 cases among American males, providing valuable insights into the dynamics of these hormonal interactions and their clinical implications.
Understanding Primary Hypogonadism
Primary hypogonadism, also known as hypergonadotropic hypogonadism, is a condition where the testes fail to produce sufficient testosterone despite adequate stimulation by gonadotropins. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, infertility, and reduced muscle mass. The condition is often diagnosed through blood tests measuring testosterone and gonadotropin levels, such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
The Role of Estrogen in Primary Hypogonadism
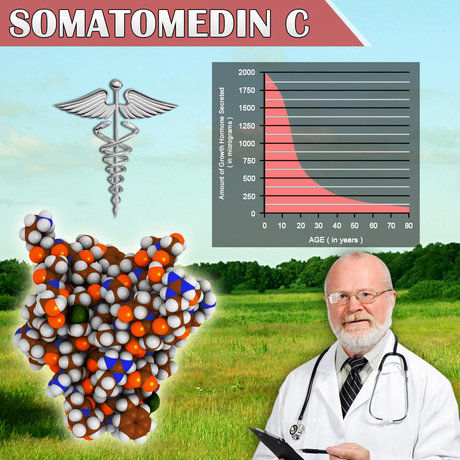
Estrogen, typically considered a female hormone, plays a crucial role in male physiology. In men, estrogen is derived primarily from the conversion of testosterone via the enzyme aromatase. The study of over 3,000 American males with primary hypogonadism revealed that despite low testosterone levels, many patients exhibited normal or even elevated estrogen levels. This paradoxical finding underscores the importance of understanding the estrogen-testosterone balance in managing hypogonadism.
Aromatase Activity and Its Implications
Aromatase is the enzyme responsible for converting testosterone to estradiol, the primary form of estrogen in humans. The study found that increased aromatase activity in men with primary hypogonadism could lead to higher estrogen levels, potentially exacerbating symptoms such as gynecomastia (enlargement of breast tissue in males) and contributing to metabolic disturbances. The data suggests that targeting aromatase activity could be a viable therapeutic approach in managing the symptoms of primary hypogonadism.
Clinical Implications and Management Strategies
The findings from this large-scale study have significant clinical implications for the management of primary hypogonadism. Physicians should consider monitoring both testosterone and estrogen levels in patients diagnosed with the condition. Additionally, the use of aromatase inhibitors, which reduce the conversion of testosterone to estrogen, may be beneficial in certain cases to restore hormonal balance and alleviate symptoms.
Future Research Directions
While this study provides a robust foundation for understanding the interplay between primary hypogonadism, estrogen, and aromatase activity, further research is needed. Future studies should focus on the long-term effects of aromatase inhibition in men with primary hypogonadism and explore the genetic factors that may influence aromatase activity and estrogen levels.
Conclusion
The comprehensive analysis of over 3,000 cases of primary hypogonadism in American males has shed light on the complex relationship between testosterone, estrogen, and aromatase activity. These findings emphasize the need for a holistic approach to managing hypogonadism, considering not only testosterone replacement but also the modulation of estrogen levels and aromatase activity. As research continues to evolve, the hope is that these insights will lead to more effective and personalized treatment strategies for men affected by this condition.
Contact Us For A Fast And Professional Response

- 0001) Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Overcoming Stigma and Enhancing Treatment [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- 0002) Primary Hypogonadism in Aging Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- 0003) Managing Primary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Challenges and Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0004) Primary Hypogonadism and Obesity Link: Impact and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0005) Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Advocacy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- 0006) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Nutritional Strategies to Boost Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- 0007) Exercise Strategies for Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- 0008) Primary Hypogonadism: Impact, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- 0009) Primary Hypogonadism: Support Networks Crucial for Emotional and Treatment Guidance [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- 0010) Innovative Therapies Transforming Primary Hypogonadism Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- 0011) Primary Hypogonadism and Sleep: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- 0012) Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Current Treatments and Future Innovations [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- 0013) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- 0014) Navigating the Emotional Journey of Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0015) Navigating Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Healthcare Advocacy in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0016) Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Work and Strategies for Productivity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- 0017) American Males' Resilience and Strength with Primary Hypogonadism: Personal Stories and Support [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0018) Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0019) Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Mass in American Males: Mechanisms and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0020) Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Treating Testicular Failure in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0021) Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- 0022) Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Causes, Diagnosis, and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0023) Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Social Life and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0024) Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0025) Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0026) Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0027) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Testosterone Therapy and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0028) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Education, Treatment, and Support for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0029) Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Image and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- 0030) Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: The Vital Role of Family Support [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0031) Community Support Enhances Life for Men with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0032) Primary Hypogonadism's Emotional Impact on American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0033) Genetic Testing for Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0034) Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Physical Activity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- 0035) Economic Impact of Primary Hypogonadism on American Men: Costs and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0036) Primary Hypogonadism: Advocacy and Research Needs for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0037) Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Self-Esteem in American Males: Awareness and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0038) Nutritionists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0039) Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Early Intervention, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0040) Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: The Vital Role of Peer Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0041) Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in the U.S. Healthcare System [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- 0042) Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Specialists, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0043) Diagnosing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Challenges and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0044) Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Males' Careers and Strategies for Resilience [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0045) Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Effects, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0046) Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0047) Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding Treatments and Managing Side Effects in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0048) Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Mental Health and Role of Professionals [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- 0049) Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Prevalence, Management, and Future Research [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- 0050) Primary Hypogonadism: Emotional Support Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- 0051) Primary Hypogonadism: Challenges and Solutions in Male Family Planning [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- 0052) Exercise Physiologists' Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- 0053) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Lifestyle Strategies for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- 0054) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Strategies for Stress and Anxiety in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- 0055) Endocrinologists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- 0056) Overcoming Psychological Barriers to Primary Hypogonadism Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- 0057) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Financial Assistance Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- 0058) Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Social Connections and Strategies for Support [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- 0059) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Education's Role in American Males' Health [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- 0060) Support Groups: Vital for American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- 0061) Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Multidisciplinary Approach [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- 0062) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- 0063) Technology Revolutionizes Primary Hypogonadism Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- 0064) Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management for American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- 0065) Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- 0066) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Challenges and Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- 0067) Mental Health Apps: A Vital Support for American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- 0068) Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- 0069) Primary Hypogonadism: Workplace Challenges and Advocacy Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- 0070) Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Hobbies and Leisure Activities [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- 0071) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Preparing for Doctor Visits and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- 0072) Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on American Males' Education: Challenges and Solutions [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- 0073) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Regular Follow-Ups in Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- 0074) Physical Therapy's Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0075) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Building Your Comprehensive Healthcare Team [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- 0076) Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Personalized Care for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- 0077) Traveling with Primary Hypogonadism: Challenges and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- 0078) Dietitians' Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males Through Nutrition [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- 0079) Five-Year Trial: Hormone Replacement Therapy's Efficacy and Safety in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- 0080) Telemedicine Revolutionizes Primary Hypogonadism Care for American Males [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]